What Are Alveolar Macrophages?
Alveolar macrophages are cells found in the lungs which are part of the immune system. Macrophages are phagocytes, which means they are able to take in and digest dead or damaged cells and potentially harmful substances such as bacteria or toxic particles. Unlike other macrophages, they are directly exposed to the environment outside the body, due to their location on the lining of the lungs. There, they help prevent infections by removing microorganisms before they enter the respiratory circulation. They also clear allergic and toxic substances from the air spaces in the lungs.
Human alveolar macrophages are the main phagocytes in what is called the innate immune system, which is the body's first line of defense against harmful microbes and toxic substances. Alveolar macrophages are able to deal with the small number of bacteria and viruses which are commonly breathed in every day. They engulf microorganisms and destroy them, and also secrete substances which attack microbes. If larger numbers of microorganisms invade the air spaces, alveolar macrophages are able to produce substances which trigger an inflammatory response, attracting other immune cells into the lungs.
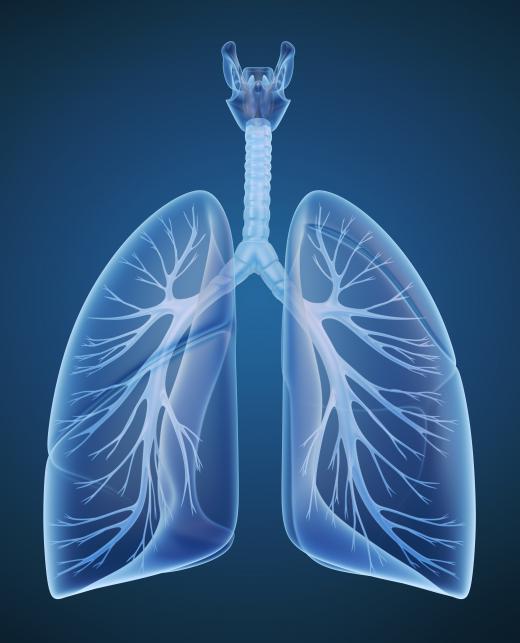
As well as initiating inflammation in order to fight disease, the human alveolar macrophage is also involved in resolving that inflammation. An alveolar macrophage cell line can produce different types of alveolar macrophage, referred to as M1 and M2 cells, which are thought to have opposing functions. M1 is the cell which is more concerned with inflammation, while M2 has more of an anti-inflammatory effect. Different situations may lead to greater or fewer numbers of each type of cell being produced.
In the course of dealing with an infection, the inflammatory response leads to white blood cells known as neutrophils dying off and collecting inside lung air spaces. The cell contents of these neutrophils could be harmful if they leaked out. As part of their anti-inflammatory function, alveolar macrophages are able to clear away the dead neutrophils before they degrade and release their contents into the lungs.
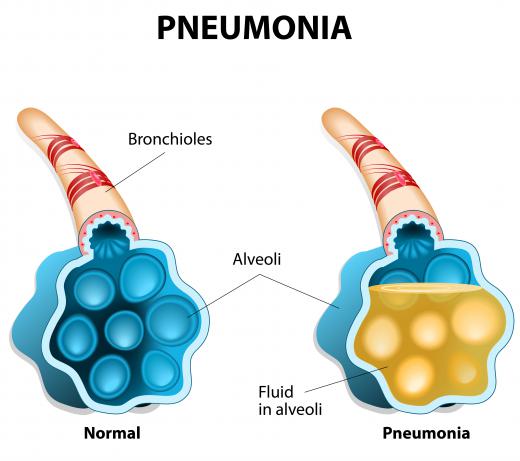
When people develop pneumococcal pneumonia, both the inflammatory and anti-inflammatory actions of alveolar macrophages come into play. A huge inflammatory response leads to the lungs' air spaces filling with fluid and neutrophils, but, thanks to the actions of alveolar macrophages, these spaces clear again without injury to the lungs. Pneumococcal pneumonia may be treated using antibiotics, or it may be prevented with a vaccine.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discuss this Article
Post your comments