What Are the Different Types of Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research refers to the use of numbers for data analysis. Different types are used in various disciplines, including epidemiology, science and medicine. The numbers can be collected manually or automatically, depending on the type of research and requisite level of accuracy and preciseness.
Also known as empirical research, the term “quantitative research” refers specifically to experiments that yield measurable values that can be analyzed using statistics, figures, and mathematical models. Numbers have quantitative properties that are used for determining average values and normal ranges for comparison. Some types of research values are tabulated manually, while other types are automated. As a result, there is some variance in the reliability of manual versus automated data collection.
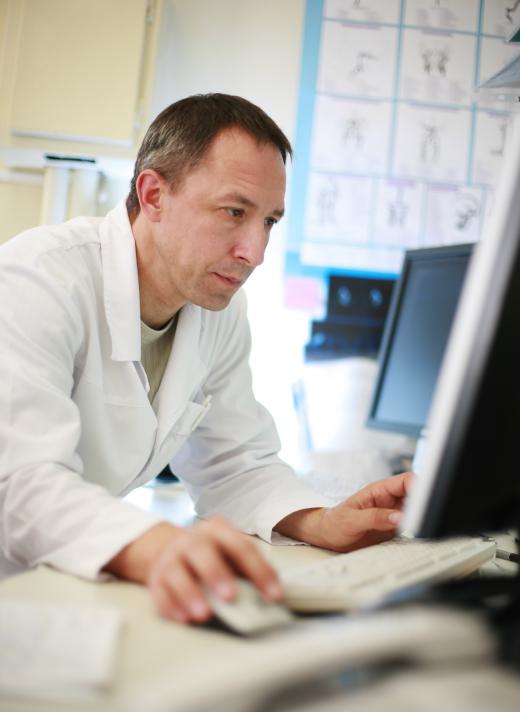

Manual data collection is generally reliable for small data sets because the margin of error is minimal. Epidemiology commonly uses survey research, a type of quantitative, manual data collection. Other forms of manual collection include the use of a timer or scale for which the measured values require accurate transcription of the reading to a data collection sheet; however, the more values there are to record, the greater the chance of human error becomes.
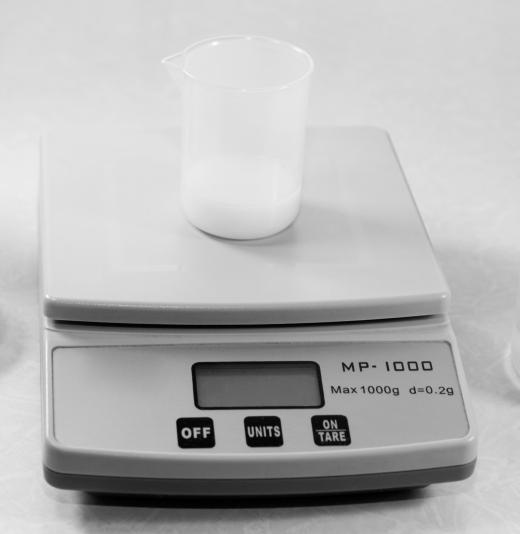

The most accurate type of quantitative research involves automated data collection in which the human error factor is nearly completely eliminated. Scientific research relies heavily on automated or computer-driven calculations for accurate and precise results. Using the previous example of a timer or scale that requires a person to transfer the reading to a data sheet, an automated system would connect the device directly to a computer and save the values without the need to write anything down.
Quantitative research has many applications in the medical field, as well. In clinical research trials, some common quantitative parameters include pathology, cardiology and physical measurements. Blood levels contain a measurable amount of white and red blood cells and electrolytes. Rather than physically counting each sample, the data collection process is automated using a computer. This increases the accuracy and preciseness of the results and also promotes consistency.
Behavioral and histological research are just two examples of how quantitative and qualitative research are used, because not everything measured will yield a real number. Qualitative research produces values based on a scale or grade. This type of data is still valuable but has less statistical power.
The ultimate goal in data analysis is to get results that can be analyzed statistically. Without numerical values, it becomes difficult to compare the results of a given study to results obtained from different studies. The use of statistics provides a universal way of interpreting the results obtained from quantitative experiments.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments