What are the Properties of Nitrogen?
Nitrogen is the element with atomic number seven. Diatomic nitrogen, or nitrogen consisting of two bonded atoms, is a clear, odorless gas that forms much of Earth’s atmosphere. It is an extremely stable molecule, resisting changes in a variety of circumstances. The boiling point of nitrogen is very low, causing it to form a gas at everyday temperatures; however, liquid nitrogen is commonly used as a refrigerant. The properties of nitrogen, including its stability and low boiling point, play a major role in both biology and human society.
Many of the properties of nitrogen result from its strong triple-electron bond. Atoms tend to be most stable when they have eight electrons in their outermost shell, or most distant region from the nucleus. A single atom of nitrogen has five electrons in the outer shell. Two atoms of nitrogen, therefore, tend to share three of these electrons with each other—allowing each atom to enjoy the stability of having eight electrons. This is the reason stability is among the properties of nitrogen.
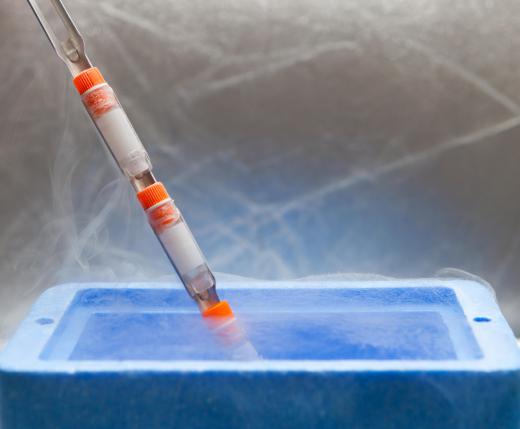
Another one of the properties of nitrogen is its low boiling point. At atmospheric pressure, nitrogen boils at -320 degrees Fahrenheit (-196 degrees Celsius). Liquid nitrogen appears as a clear liquid similar to water. It can be stored in special freezers and brought into open air for brief periods of time before it fully boils off. Technicians often use liquid nitrogen as a cryogenic refrigerant, or a substance that can cool down other equipment or devices.
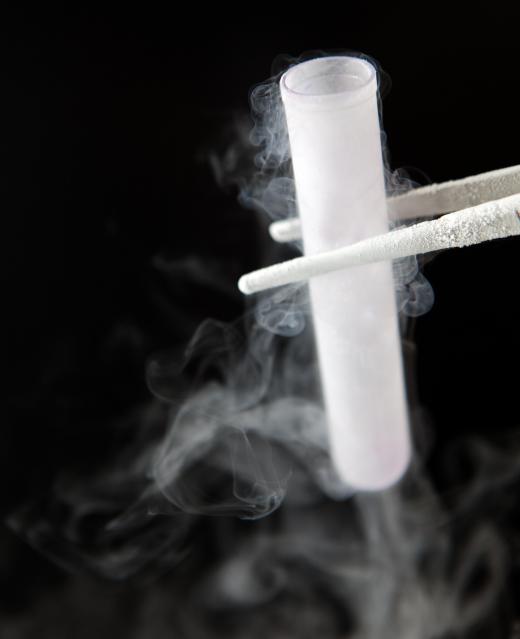

In the earth’s atmosphere, nitrogen constitutes 78.1% of the air by volume. Most of this diatomic nitrogen, however, is unavailable for use by organisms because it is in its stable, molecular form. Some bacteria can break nitrogen’s triple bond and attach hydrogen and oxygen molecules to a single nitrogen atom. The properties of nitrogen allow energy to be released when plants and animals use these bacteria-formed compounds. Finally, some bacteria can return nitrogen to its original form and release it into the atmosphere, a process known as the nitrogen cycle.
Human beings, having evolved in an atmosphere dominated by nitrogen, rely on the element for basic biological functions. The properties of nitrogen are also useful in industrial applications. When combined with hydrogen or oxygen, nitrogen can form compounds that burn or explode, releasing energy as heat. When combined with carbon, nitrogen forms cyanide, which is useful in mining and medical applications. Yet, nitrogen can be dangerous if improperly handled—a number of precautions are necessary to safely work with nitrogen.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
this was okay but it wasn't helpful to me much.
I am currently doing a project on the element nitrogen and need to know what are the most common forms of the element when used by humans and how is it used, but in this article it didn't really tell me an answer to it. Can you please help me A.S.A.P. Thanks this is very appreciated.
Post your comments