What are the Properties of Oxygen?
Oxygen is among the most abundant and most important elements on the Earth. Many of its properties make it very important to the composition and continuity of various systems throughout the universe. Oxygen is a highly reactive element; it is involved in a massive variety of different chemical reactions and is absolutely integral to many of the chemical processes that occur nonstop around and throughout the Earth. The specific properties of oxygen at a microscopic level, such as allotropy and electronegativity, make it essential to life itself and to many organic chemical processes that are necessary for life.
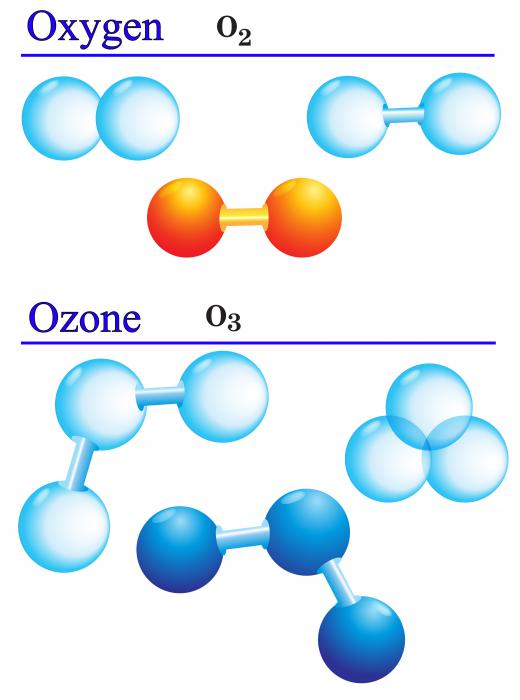
When discussing oxygen, it's common to refer to it in its gaseous form, though other forms do exist. This element normally exists as two oxygen atoms that are bound together and exist as a gas. At particularly high pressures, it can be compressed to liquid and solid forms; this is rare, however, and seldom occurs in nature. Diatomic oxygen, also known as molecular oxygen, is colorless and odorless. It is essential to many processes that occur in living creatures, specifically cellular respiration.

Allotropy is one of the important properties of oxygen. Allotropes refer the different ways that a single element can be combined to form molecules. Diatomic oxygen, O2, is the most common allotrope, and O3, ozone, is another gaseous form that is highly reactive and abundant in Earth’s atmosphere. O4 and O1 are both relatively unstable allotropes; O1 atoms, in particular, are known as free radicals and are extremely reactive. Solid oxygen can exist in many different forms, including as O8.
There are many different chemical compounds that contain oxygen atoms. Water, with the chemical formula H2O, is likely the most prevalent example as it is visible in mass quantities across the Earth. There are several properties of oxygen that lead it its high reactivity and ability to form compounds. It is, for example, highly electronegative, meaning that it is able to attract electrons to itself. Chemical bonding occurs when electrons are transferred or shared, so high electronegativity generally leads to high reactivity.

Combustion is one of the many different kinds of reactions that oxygen is often involved in. In combustion reactions, a fuel is oxidized, meaning that it is broken down chemically, and part of it is replaced by oxygen atoms. This is why a candle stops burning when it is covered and removed from an oxygen source. Usually, some initial source of energy is necessary to cause a combustion reaction to occur. Similar reactions involving oxygen are also involved in the essential energy-producing processes in organisms, such as cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments