What Is an Antibody Conjugate?
An antibody conjugate is a tagging molecule that can be used in histological or enzymatic antigen detection assays to localize bound antibodies. It functions by being physically attached, or conjugated, to the antibody that is used to tag an antigen of interest. An antibody that is tagged to an antibody conjugate is a tool often used in research to identify either the exact location or the quantity of proteins or antigens of interest, against which the antibody or antibodies were raised.
Histological and proteomic assays often rely on antibodies as a reagent in research techniques by which specific proteins can be labeled. By exposing an antigen or protein of interest to an antibody that was raised against it, antigens or proteins can be tagged. By using an antibody conjugate — that is, an antibody that has been conjugated to a molecule specifically used or synthesized to be easily detected — antibodies on their respective antigens can then be identified and assayed. The most common type of antibody conjugate is a fluorescent molecule, allowing for identification of antigens in tissue under a fluorescent microscope. Other conjugates include molecules like horse radish peroxidase, which is used in conjugation with antibodies for later development with diaminobenzidine (DAB).
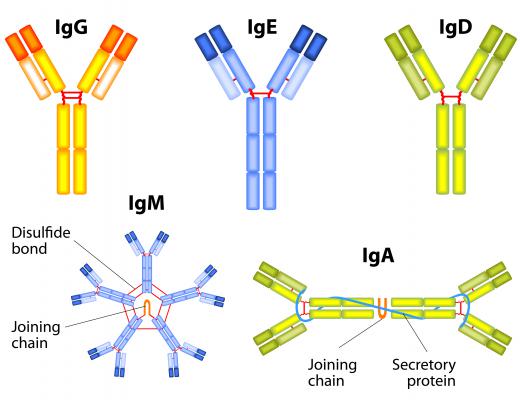
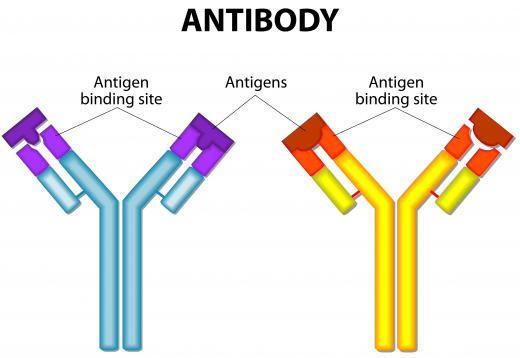
Often primary antibodies will be raised against specific antigens, while secondary antibodies will be conjugated to tagging molecules and raised against the primary antibody. As an example, one might be interested in identifying an antigen called Antigen X. One would then use, for example, an antibody raised in a mouse that reacts and sticks to Antigen X. To be able to find where these primary mouse antibodies have found and bound to these Antigen X molecules, a secondary antibody would then be used — for example, one raised in a goat — that would be tagged with a conjugate that makes this secondary antibody detectable in either enzymatic or fluorescent microscopic assays. For assays in localizing antigens using an electron microscope, gold particles are often used as an antibody conjugate because they can be detected using an electron beam.

The reason for using primary and secondary antibodies, instead of using an antibody conjugation in which the primary antibody is directly conjugated, is cost effectiveness. Antibody conjugation is expensive in terms of time and reagents. Especially for uncommon antigens, antibody conjugation on primary antibodies is not worth the expense of production. Rather, by using antibody conjugation on secondary antibodies, large amounts of a conjugated antibody can be synthesized at once and used in assays with a range of primary antibodies tailored to localize many different antigens, making the production process worthwhile and cost-effective.
In some cases, however, a primary antibody will be tagged to reduce the noise in the detection signal due to the heightened non-specific antibody binding that results from using multiple antibodies. While this expensive, highly sensitive assays will still call for this method. It is possible to purchase kits that allow a researcher to tag conjugates to their own antibody of choice, increasing the cost of the reagent, but reducing the protocol steps and possibly increasing the signal-to-noise ratio in the final antibody detection assay.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments