What is Cadmium?
 Mary McMahon
Mary McMahon
Cadmium is a rare metallic element found in small deposits on almost every continent. It has a number of uses, perhaps most famously as a pigment in paint, and it can be expensive due to its rarity. This element is also toxic, and it should be handled with care; people who are exposed to cadmium because of their occupations should exercise routine cautions, as it will bioaccumulate, concentrating in the body without being eliminated like other toxins are.
Pure cadmium is rare in nature. The element is usually found in combinations with other elements, typically copper, zinc, and lead. It is extracted from these ores during the smelting process, or with the assistance of chemicals such as sulfuric acid. When isolated, cadmium is a soft, bluish white metal that is highly ductile, making it extremely suitable for metal alloys. The element's atomic number is 48, and it is identified on the periodic table of elements with the symbol Cd, among the transition metals.

Fredrich Stromeyer identified cadmium in 1817, when he was studying zinc and its impurities. The element is named for the Greek god Cadmus, who had an adventurous life around 2000 BCE, according to Greek mythology. Initially, the toxicity of cadmium was not recognized, and it was even used as a medical treatment until scientists realized how harmful the element was. This practice is actually surprisingly common with many chemical elements, such as lead and arsenic, both of which were used in makeup compounds historically.
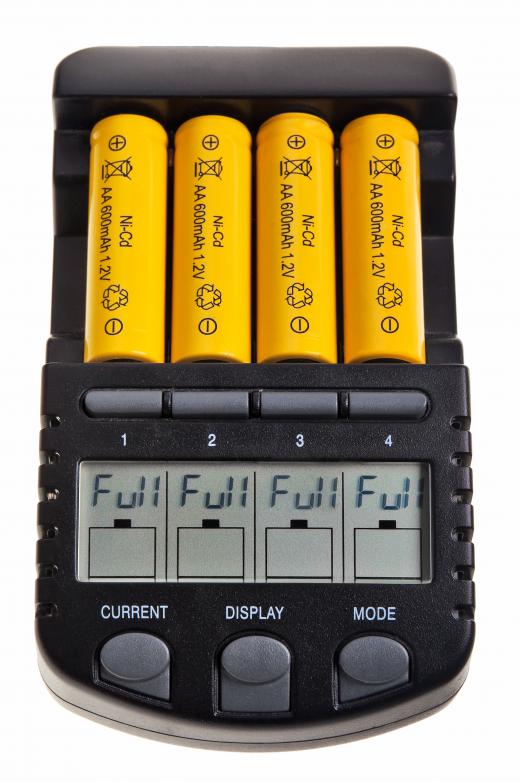
Most of the world's cadmium is used in the production of batteries, particularly rechargeable batteries such as nickel-cadmium batteries. It's also used to create yellow, orange, and red pigments, and it is sometimes added to plastics as a stabilizer. The element is also used in alloys, solders, and some semiconductors, and there are numerous uses for its compounds as well as the element itself.

Cadmium and its compounds are generally considered to be carcinogenic by most health and safety agencies. The element irritates internal organs such as the lungs and intestines when inhaled or ingested, and long term exposure to high levels can cause death. People are exposed to metal through occupations that involve its use, along with polluted air and water. Once cadmium has polluted an area, it can also be very difficult to remove; this is a major issue in areas where the metal is mined and processed.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discussion Comments
@StarJo: You think they polluted the river on purpose, or because of the lack of environmental monitoring by government officials means that factories making cheap crap for the western market can carry on doing so?
If you look closely at the factories and the products they make, it will surely be an American business getting these factories to make a product they can ship home and thus polluting somewhere else due to the strict pollution guidelines within the U.S.
You would think with the way the size of a soda is being regulated in New York I think it is, that the seriousness of cadmium would be made more aware to the public, or even its use restricted.
Cadmium is one of the carcinogens in cigarettes. I'm so glad that my husband quit smoking after only six years, because he has spared his body from the many horrible effects of carcinogens.
Cadmium damages the lungs, and we all know that this is what cigarettes are infamous for doing. It also hurts your other organs and eventually kills you.
I have read that cadmium can mess up your senses. Maybe this is why my husband's sense of smell was so dull before. He has regained it since he quit, but it took awhile.
My sister quit smoking as well, and she told me that all those years, she never knew how bad her clothing and house had smelled. After quitting, she could smell cigarette smoke on everything.
I heard about an incident of cadmium pollution in a river in China that killed millions of fish. What's even worse is that this river was where people got their drinking water from, so you can imagine how everyone panicked.
Some businesses along the river were to blame. They dumped waste into the river that contained cadmium. I think this is very dumb, because they were polluting their own drinking supply.
You can bet that millions of people ran out and stocked up on bottled water after hearing this. Some kind of neutralizer was used to treat the river, but still, it would be hard to trust that it was safe to drink again so soon after the incident.
@wavy58 – You are really only in danger from cadmium when you breathe it in or eat it, so you don't have to worry too much about cadmium poisoning when touching it. I've read that your skin doesn't easily absorb it.
However, it might be a good idea to wear gloves when painting with cadmium paint. This is just because you might have small cuts or openings in your skin, and the cadmium could get into your blood through these.
In general, though, batteries are safe. Just don't handle battery acid, and you should be fine.
I had no idea that cadmium was toxic! I have some cadmium yellow acrylic paint that I use often, and I've gotten it on my fingers several times. I am now scared that I may have been poisoning myself a little bit.
I'm also a little freaked out about the cadmium in batteries. Can you absorb it just by handling the exterior of a battery while replacing one? If so, then I am going to start wearing gloves while touching batteries!
I suppose that I could be wearing disposable gloves while using cadmium paint, too. I will start protecting myself, now that I know how dangerous cadmium can be.
Post your comments