What Is Methylation?
Methylation is a type of chemical reaction during which methyl groups are added to other molecules. A methyl group has the formula CH3, representing its structure as a carbon atom that has three hydrogen atoms single bonded to it. Referred to as functional groups, methyl groups are just one example of an alkyl group, which all have single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. The number of carbon atoms in the backbone of the alkyl group determines which one it is. Functional groups are the parts of molecules that cause the characteristic chemical reactions associated with the molecule.
As methyl is an alkyl, methylation is a form of alkylation. During an alkylation reaction, the specific alkyl group is attached to the molecule by replacing a hydrogen atom. In methylation, the methyl group is the functional group that replaces the hydrogen. There are hundreds of different methylation reactions that occur in biological systems.

In biological systems, methytransferase enzymes are needed to catalyze this chemical reaction. Many different types of molecules undergo methylation with the assistance of enzymes, including DNA, RNA and proteins. The pattern is established during embryonic development and continues throughout life as methyl groups are continuously lost and added to the relevant molecules. This is a natural process that is involved in regulation of gene expression, protein functioning and the metabolism of RNA. If this process did not take place, detrimental health effects could occur.
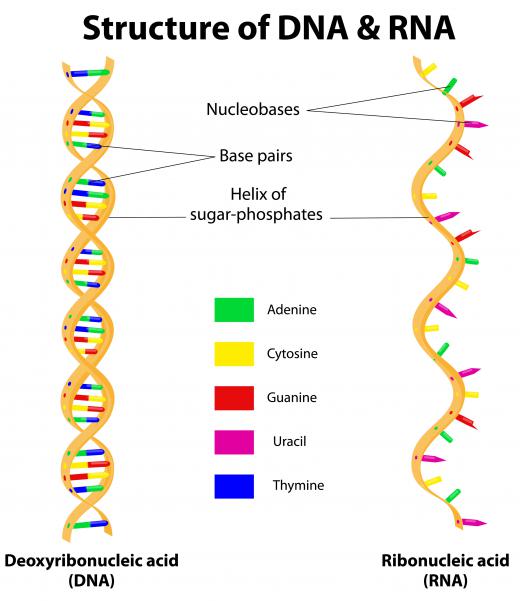
A number of genetic defects has been linked to abnormalities in this process. If there is a mutation in the methyltransferase enzymes, ICF syndrome can result. This syndrome is extremely rare and symptoms include low set ears, an enlarged tongue, and an increased distance between the eyes. This is an immune disorder that results in low levels of antibodies, so many patients die from infectious disease before they reach adulthood.
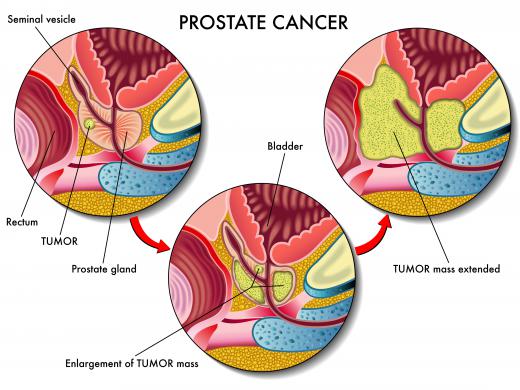
Some forms of cancer have been associated with high or low levels of methylation of certain genes. Whether a gene has been methylated is used as a marker for some forms of cancer — one example is prostate cancer. If there is an abnormality in the methylation of a gene that controls cell division, this can lead to uncontrolled cell division, or tumor growth. Furthermore, if there is a mutation in the gene that codes for DNA methyltransferase, this can lead to a proliferation of the enzyme, which can in turn lead to an increase in methylation of a particular gene.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments