What is Nitroaniline?
 Karyn Maier
Karyn Maier
Nitroaniline is an organic chemical compound consisting of a phenyl group and an amino group. Nitroaniline occurs as a stable, water-soluble powder that ranges from yellow to brown in color and gives off a slightly amine aroma. This organic compound is known by numerous other chemical names, including p-Aminonitrobenzene, PNA, 4-Nitroaniline, 1-amino-4-nitrobenzene, p-aminonitrobenzene and diazo fast red gg, in addition to several trade names. However, this amino chemical compound is most commonly referred to as p- Nitroaniline.
Nitroaniline has several applications in various industries. It is commonly used as a chemical intermediate in the manufacturing of dyes, pesticides, gasoline, certain pharmaceuticals and poultry medications.
Working with nitroaniline presents certain occupational hazards. As a powder, it is very reactive to static discharge in the atmosphere, which makes it highly combustible. In fact, nitroaniline has been known to set off dust explosions. In addition, nitroaniline is moisture sensitive, making it vulnerable to igniting spontaneously in reaction to coming into contact with other chemicals. Should a fire occur, it should be extinguished with water, foam, or carbon dioxide.

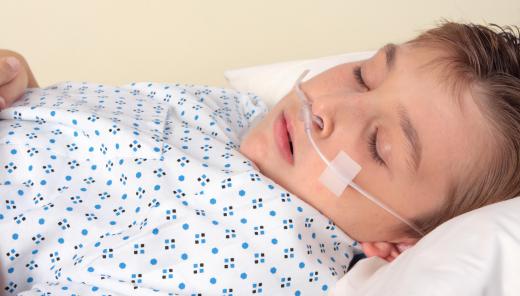
Nitroaniline is highly toxic to humans. While the incidence of accidental release is relatively low because the compound is a powder, it is still considered a toxicity risk due to the fact that it is readily absorbed though the skin. Nitroaniline is also toxic if it is inhaled. Exposure to this organic substance can result in a condition called methemoglobinemia, which is characterized by changes in the blood. Specifically, hemoglobin is converted into methemoglobin. This results in the impairment of blood cells and a reduced capacity to transport oxygen.

Symptoms of toxicity may occur as late as 12 hours after exposure and include respiratory distress and cyanosis, or a blue discoloration of the skin due to oxygen deprivation. Standard treatment of nitroaniline exposure consists of rest and respiratory therapy until serum methemoglobin reverts back to normal hemoglobin and oxygen delivery is restored several hours later.

Nitroaniline should only be handled under a vented hood and while wearing safety glasses, as well as protective clothing and gloves. This substance is reactive with reducing and oxidizing agents, as well as sodium hydroxide, and care should be taken to prevent cross contamination. Nitroaniline may also damage certain plastics and rubber materials. Unused amounts of this organic material should be treated as hazardous waste and stored and disposed of accordingly.
Nitroaniline is considered to be an environmental pollutant with long-term negative impact. In particular, nitroaniline is known to be toxic to marine life.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments