What is Optoelectronics?
Optoelectronics is a branch of electronics that deals with converting electrical energy to light and converting light to electrical energy by way of materials called semiconductors. Semiconductors are solid crystalline materials with electrical conductivities that are lower than those of metals but greater than those of insulators. Their physical properties can be modified by exposure to different types of light or to electricity. In addition to visible light, forms of radiation such as ultraviolet and infrared light that are not visible to the human eye can affect the properties of these materials.
One of the earliest physics discoveries that led to the development of modern optoelectronics is known as the photoelectric effect. The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons by a material when it is exposed to certain types of light. When the material absorbs sufficient energy in the form of light, electrons can be bumped from the surface of the material, thereby generating an electrical current and leaving behind electron holes. A related phenomenon is the photovoltaic effect in which absorbed light causes a material’s electrons to change energy states, thereby creating a voltage that can generate electrical current.
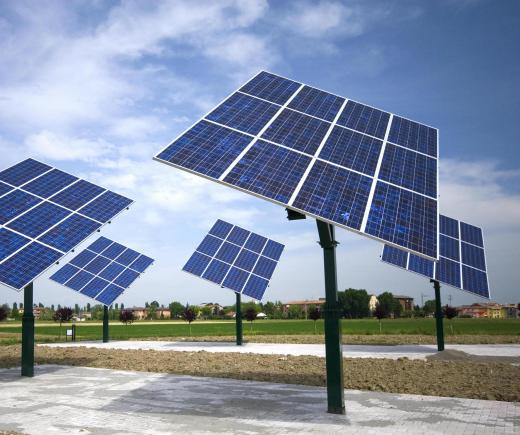

Solar power generation by solar cells that absorb light from the sun is a common application that takes advantage of these effects. Electricity generated in this way can be used directly or stored in batteries for later use. Practical applications of solar cells include power generation both on earth, such as for off-grid homes in remote locations, and in space, such as for satellites.
Electroluminescence is another important effect that is made use of in optoelectronics. When electricity is applied to certain materials, it drives electrons in high-energy states to combine with electron holes and fall into more stable states of lower energy, thereby releasing energy in the form of light. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are a common example of the use of electroluminescence. LEDs in a variety of colors are used as power-on indicators, in digital displays for such items as calculators and home appliances, for illuminating signs and traffic lights, as headlights and signals on cars, and more. Dashboard instrument panels in vehicles also commonly make use of electroluminescence for lighting.

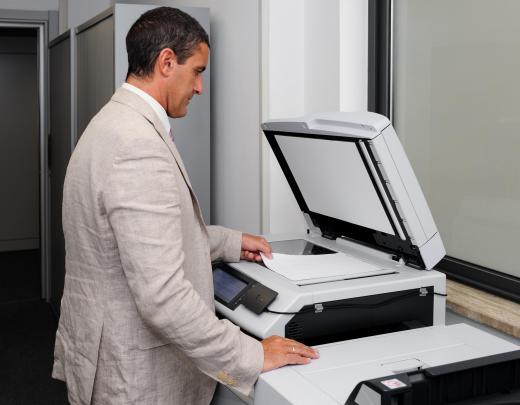
Photoconductivity is the phenomenon of increased conductivity of a material under illumination. This effect varies with greater light intensity generating more electrons and electron holes in certain materials, thereby raising the electrical conductivities of these materials. Photocopier machines were made possible through the application of this particular phenomenon of optoelectronics. When a photoconductive surface in a photocopier machine is exposed to an image, a difference in conductivity is created between the illuminated areas that do not contain the image and the non-illuminated sections that do. As a result, powder in the machine is distributed in the form of the image, after which it is fused to a piece of paper to complete the copying process.

These and other optoelectronic effects are integrated into a vast array of devices and applications in numerous combinations, with even more in development. Many industries have been revolutionized by the application of optoelectronics. Optoelectronic devices play a critical role in applications and products from computers to communications, medical technology to military equipment, photography and other imaging techniques, and beyond.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments