What is Pyrimidine?
Pyrimidine is group of molecules that are part of the DNA and RNA structure. These molecules feature a single ring structure made of six atoms. There are several pyrimidine molecules, but only cytosine and thymine are part of the DNA structure, while cytosine and uracil are part of the RNA structure. These molecules bind with their purine counterparts to join the two strands of the DNA or RNA polymer. Drugs that are similar to pyrimidine have been used to treat a certain conditions including skin cancer and keratosis.
Cytosine, thymine and uracil feature a six membered ring structure. Uracil has two oxygen atoms attached to the ring. Cytosine has one oxygen atom and one amine group (-NH2) attached to the ring, while thymine has two oxygen atoms and a methyl group (-CH3) attached to the ring. The ring structure of each of these pyrimidine molecules contain two nitrogen atoms and four carbon atoms.
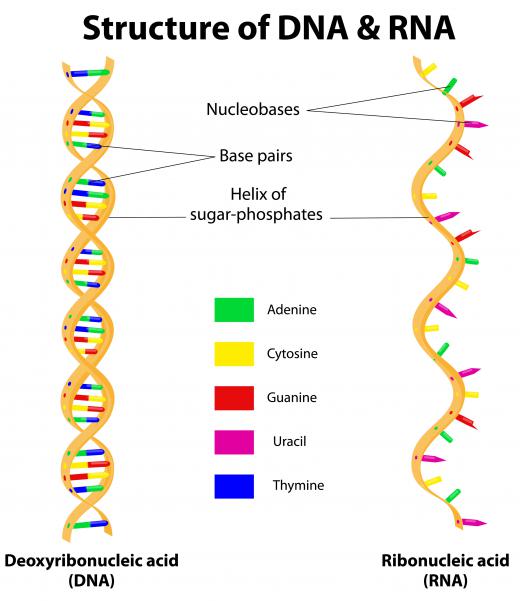
The pyrimidines bind with the purines to join the two strands of the DNA or RNA polymer. Adenine and guanine are the purines and each one features a five membered and a six membered ring that are joined together. In DNA, cytosine binds with guanine, and thymine binds with adenine. The connection between cytosine and guanine is made of three hydrogen bonds, while the connection between thymine and adenine features two hydrogen bonds. In RNA, uracil takes the place of thymine and binds with adenine.

When a sugar group is bound to a pyrimidine or a purine, it is called a nucleoside. Deoxycytosine and (deoxy)thymidine are the pyrimidine nucleosides and deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine are the purine nucleosides. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose, which is a five carbon sugar molecule that lacks the hydroxyl group (-OH) normally present in the ribose sugar molecule. With RNA, the sugar molecule is ribose, and the nucleosides are generally named without the 'deoxy' prefix.
A complete nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, which is the pyrimidine or purine, a sugar molecule and a phosphate group. The phosphate group binds to the sugar molecule of a nucleoside through an ester linkage. One nucleotide is bound to another nucleotide by a phosphodiester bond.
Flurouracil is a drug that is similar in structure to the pyrimidine uracil. It is usually used to treat a specific type of skin cancer called superficial basal cell carcinoma and other skin ailments, including scaly or crusted lesions caused by too much sun exposure. The drug is usually sold in the form of a cream.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments