What is Visible Light?
 Michael Anissimov
Michael Anissimov
The visible portion of the spectrum is that which can be perceived by the human eye. It is slightly different for each person, although light with a wavelength of 400 to 700 nm is the usual definition. Some people are able to see visible light with wavelengths as short as 380 nm and as long as 780 nm. There is a repeatable experiment in which humans are able to perceive x-rays, which have wavelengths as short as 0.1 to 10 nm, but the visibility may derive from second-order interactions that produce light in the visible range.
The portion of the spectrum where visible light can be found corresponds closely to the short-wavelength (less than 5 cm) light that best penetrates the Earth atmosphere's optical window. If humans evolved on a different planet with a different optical window, the range would likely correspond closely to that light which passes through the atmosphere easiest.
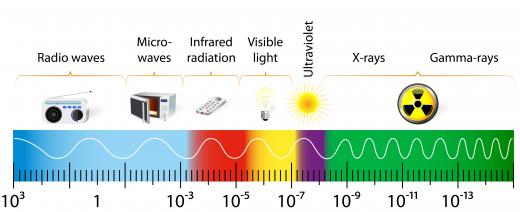
The existence of a distinct spectrum was most famously demonstrated by Isaac Newton in his early experiments with prisms. He showed that white light is actually a composite of various types of light in the visual spectrum. These are also the colors that appear in the rainbow. A mnemonic for the visual spectrum is ROY G BIV: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. The human eye is most sensitive to green light, with a wavelength of about 555 nm, probably an adaption to help people navigate in environments rich with greenery, such as forests and jungles.

Brown, pink, and magenta are absent from the visible light spectrum, because they are not true physical colors, but instead emerge from certain combinations of light, especially red. The optic nerve and visual cortex are among the best studied areas in the human brain, giving us unique insight into how people process light.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discussion Comments
@ Fiorite- The phenomena you witnessed has everything to do with the wavelength of light. Sunlight emits all of the different wavelengths of visible light (as well as some invisible wavelengths) in a continuous spectrum. This is why rainbows are created (the raindrops act as prisms). Artificial light on the other hand only emits some wavelengths of light, depending on the elements used within the bulb. Since artificial light does not emit a full spectrum of light, it shows up as a line spectrum. the gaps between the lines are the wavelengths that the light source does not emit.
If you could somehow create a rainbow with artificial light, it would look like an arc of banded colors with gaps in between and missing colors. This is also why artificial light will sometimes cast a slight yellow, blue, or orange hue on things.
I have a question for anyone out there who might be able to answer it. Why does a prism emit a rainbow of colors when it diffracts sunlight, but only colored lines when it diffracts artificial light? I noticed this the other day as I was messing with a prism that was sitting on my desk (My wife gave it to me). I would be interested to know if there is a reason for this, or if it is just the way that I was holding the prism. Does it have anything to do with the wavelength of visible light?
I never knew that the human eye was most able to see the color green on the visible light spectra. This was a very informative and interesting article.
Post your comments