What is Ultraviolet Light?
Light consists of waves of energy that are able to move without the presence of a medium to travel through. Light energy has both electric and magnetic fields, so it is often referred to as electromagnetic radiation. Light waves come in many sizes, or wavelengths. The light we can see is only a very small part of the spectrum of light waves that exist. Ultraviolet light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum beyond visible light.
Humans cannot see ultraviolet light, but some insects, such as bees, can. UV light has a shorter wavelength, higher frequency and higher energy than the light within the visible spectrum. Wavelength is the size of the wave, or the distance between two corresponding points on waves – peak to peak or trough to trough, for example. The frequency is the number of waves that pass a certain point during a specific time interval, usually one second. Frequency is directly related to energy, so the higher the frequency of the wave, the higher the energy and vice versa.
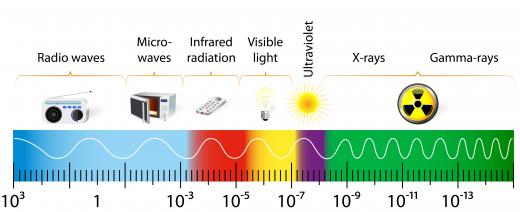
Depending on the frequency of the light, different colors are produced. In the visible spectrum, the colors range from red, at the lowest frequency of visible light, to violet. Ultraviolet light is so named as it is beyond violet. It has a shorter wavelength than violet light and a higher frequency and energy. X-rays come after UV light on the electromagnetic spectrum.
The UV light spectrum can be divided in a number of different ways. Scientists refer to near, extreme and far UV light, based on the wavelength of the light and how energetic it is. UVA, UVB and UVC are also used to categorize ultraviolet light. Again, the categories are determined by the length of the wavelength and energy. UVA or near UV light has the longest wavelength and least energy, while extreme has the shortest and most energy.

Most of the ultraviolet light on Earth comes from the sun. When UV light reaches the atmosphere, it reacts with oxygen molecules to create ozone. This reaction is what causes the ozone layer to form above the Earth. The ozone layer can be anywhere from six to 31 miles (10 to 50km) above sea level. Almost all of the short wave ultraviolet light is absorbed by the ozone layer before it can reach the Earth’s surface.
Longer wavelength ultraviolet light, or UVA, is able to pass through the ozone layer and continue to the surface. This type of UV light is what causes suntans and sunburns. These wavelengths are essential for a healthy human life as they cause the production of vitamin D in the body. This in turn is used to form healthy bones and teeth. UV light can also be used to help treat skin conditions, such as psoriasis.
Too much exposure to ultraviolet light will have detrimental effects. UVB light causes sunburn and some types of skin cancer. The most dangerous of skin cancers are due to damage to the DNA of skin cells caused by UVB light. All types of UV light also affect collagen, resulting in premature aging of skin.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments